The popularity of terrace construction has grown, and there is a demand for higher-quality wood materials. Many people want to consider both durability and environmental friendliness when choosing a material, and these two perspectives are nicely combined in thermally modified wood.
Impregnated wood has dominated terrace construction for a long time and is familiar to most Finns. In recent years, however, there have been more options in the terrace board selection – and one of the strong risers is thermally modified wood.
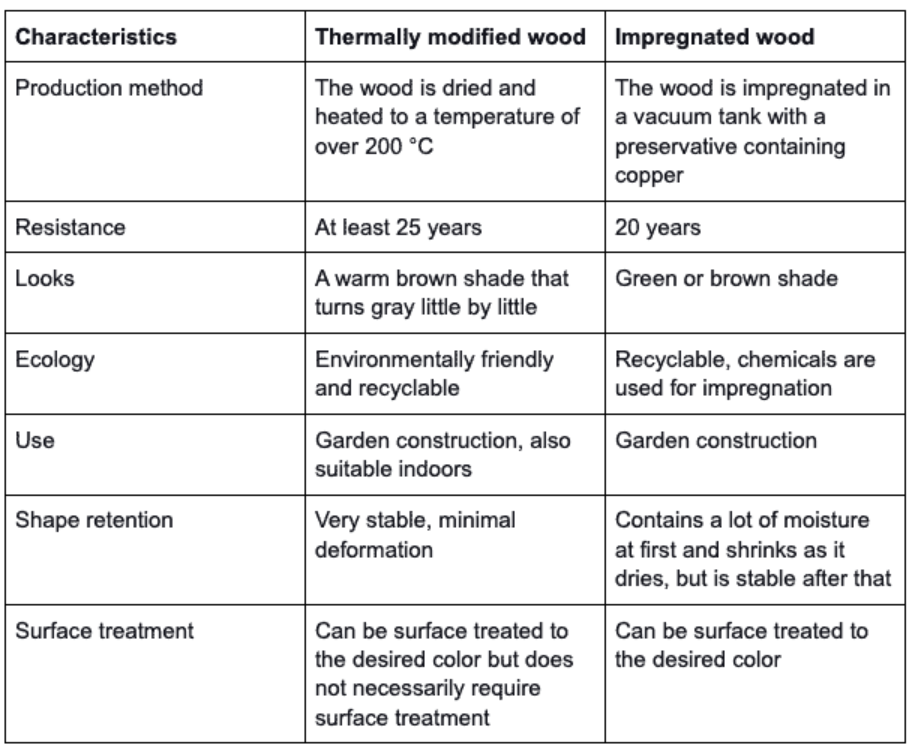
Thermally modified wood is often compared to impregnated wood because they both have been modified to withstand the conditions better than ordinary wood. Thermally modified and impregnated wood have many similarities but also many differences.
Thermally modified wood combines all the properties required of a modern material
Thermally modified wood is nothing new: thermal modification technology was developed in Finland in the 1990s. However, most of the thermally modified wood produced in Finland has been exported abroad because of the greater demand.
The thermal modification makes the wood extremely durable. First, the wood is dried, so its moisture content drops to zero. Then follows the heat treatment, during which the structure and properties of the wood change completely:
- The wood no longer absorbs moisture as much as it normally does.
- The stability of the wood improves.
- The wood´s biological resistance increases, so pests and small organisms can no longer utilize it.
- The wood is lighter and has a lower density, making it easier to work.
Thermally modified wood has gained more foothold in the Finnish market as its advantages have become more familiar to builders. In terrace construction, thermally modified wood is an increasingly common choice. It is also used indoors in wet areas. Thermally modified wood is especially preferred for balcony use due to its dimensional stability and minimal deformation.
Using thermally modified wood is an environmental act
One of the apparent strengths of thermally modified wood as a construction material is its environmental friendliness. Producing thermally modified wood does not require any chemicals, so it is a non-toxic and safe material for both installers and end users.
Thermally modified wood is a carbon-negative product, which means that the product slows climate change. It binds more carbon than it causes carbon dioxide emissions.
For us at Siparila, the advantages of thermally modified wood are obvious. That is why we also asked the customer's point of view. Nastarakennus Oy from Oulu, known for investing in high-quality construction, is currently making material choices for their residential property and is strongly considering using thermally modified wood for terrace planking. "Fregattipiha is a unique property, completed in a great location by the sea, so we are also looking for durability and quality in the selection of materials," says project director Risto Kamula.
"Choosing thermally modified wood is supported by many of its good features. It is indestructible, durable, dimensionally accurate, and keeps its shape. We want to think in the long term: when we choose a high-quality material, there is no need to repair it afterward and receive complaints. Maintenance freedom is also important because we think about the end user's benefit", Kamula continues.
"On the other hand, the installer's work gets easier and more efficient because the thermally modified wood bundle does not freeze like impregnated wood. It should be possible to install it without worry, even in winter."
How does impregnated wood differ from thermally modified wood?
Impregnated wood is produced by using chemicals. In this way, the wood becomes better resistant to decay than untreated wood, and its service life gets 3–5 times longer.
In terms of durability, impregnated wood is a good and functional material, but its flip side is the burden it causes on the environment. However, wood impregnation in Finland takes place according to precise regulations, and the impregnation agents used today are copper salts and active organic substances. Impregnated wood must always be recycled and is not recommended for use outside.
Thermally modified wood can also be recycled, but since it does not contain chemicals, recycling points accept it free of charge. Alternatively, thermally modified wood can be burned or chopped into compost.
Properties of thermally modified and impregnated wood in comparison:
Siparila combines the advantages of thermally modified wood and hidden fastening
Larch used to be the primary material of Siparila's selection of terrace boards, but after its availability decreased, we started using thermally modified wood. These materials share many of the same excellent properties, but thermally modified wood takes them further.
In thermally modified Thermodeck terrace boards, durability and stylish appearance go hand in hand. Thermodeck Classic with a flat surface is a simple and discreet design, while tiny grooves enliven Thermodeck Elegant's surface. Both options are available in top-mounted and concealed fastening.
Concealed fastening enables the surface of the terrace to be completely flawless. The boards are attached with hidden clips, resulting in a neat and uniform surface where no nails are visible.
Ask more about Thermodeck products directly from us or or our distributors.

